Introduction
Companies are becoming increasingly aware of the environmental and social costs that may be involved in the production of goods. Usually, these costs are not included in the final cost of the goods and are known as 'externalities'. Externalities include, for example, the depletion and pollution of water sources and waste from production processes.
The goal of this project was to develop standard methods for the valuation of externalities associated with the production and consumption of commodities, and to provide evidence for policy engagement about the sustainable and equitable management of natural capital.
This project was undertaken by the Valuing Nature Network, the Cambridge Programme for Sustainability Leadership and the Natural Environment Research Council.
Case studies
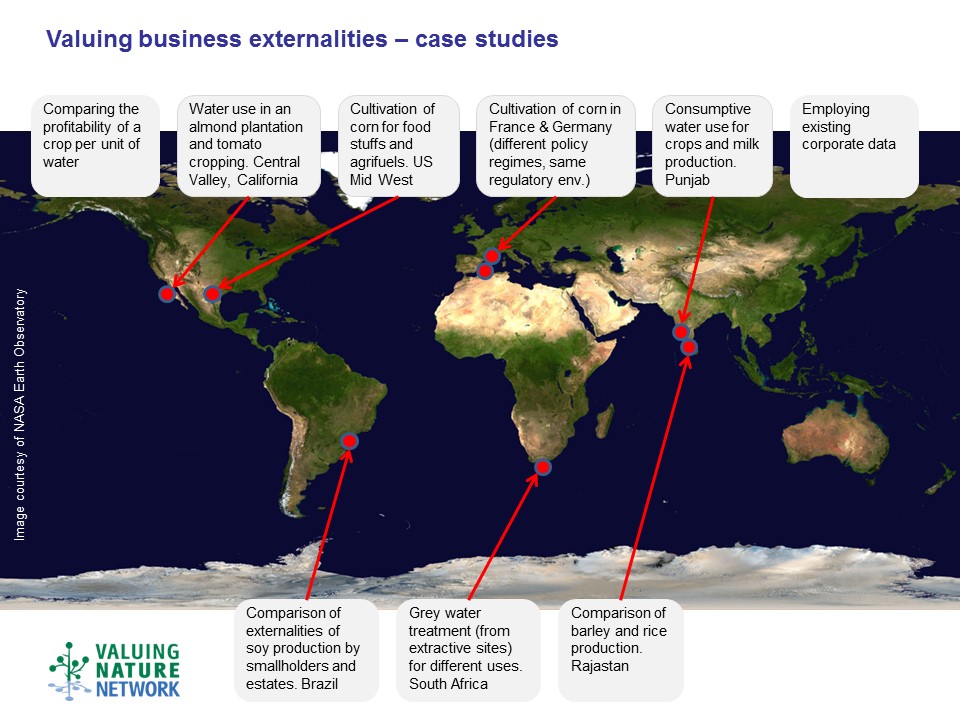
The project brought together 12 major businesses across a number of sectors and economists and ecologists from the Valuing Nature Network interdisciplinary community to conduct detailed case studies.
The work was based on is two exemplar studies: the value chain of cereals and the use of water.
The project was co-funded by the Valuing Nature Network and the Cambridge Programme for Sustainability Leadership, with additional funding from the Natural Environment Research Council.
Aims and Objectives
The objective of the project was to develop and test useable methods for the valuation of ecosystem-related externalities in collaboration with global business.
Aims
The project aimed to develop standard methods for the valuation of externalities associated with the production and consumption of commodities.
The project linked to 12 major businesses across a number of sectors.
The Valuing Nature Network interdisciplinary community was engaged to conduct detailed case studies.
Outputs
Published papers:
SABMiller Case STudy - The (Sustainable) Business Case for Natural Capital Valuation
E.Valu.A.Te Summary and Signposting
E.Valu.A.Te Listening to Business
The Cambridge Programme for Sustainability Leadership have also produced an Evaluate Game - to view the promotional video and start playing, please visit their website.
The team
Project leader
Dr Bhaskar Vira - University of Cambridge
Each case study involves one economist and one ecologist, who form the research team working with the business partner.
Water case study teams:
1. Water use, almond/tomato in California
Economist: Andy Thorpe - Portsmouth
Ecologist: Alison Holt - Sheffield
2. Water use crops/milk in Punjab, India
Economist: Dan van der Horst - Birmingham
Ecologist: Colm Bowe - Liverpool John Moores
3. Grey water in South Africa
Economist: Andy Thorpe - Portsmouth
Ecologist: Zbigniew Grabowski
4. Crop profitability per unit of water
Economist: Bruce Horton - consultant
Ecologist: Alison Holt - Sheffield
Crop case study teams:
1. Corn in France & Germany: food and biogas
Economist: Steven van Passel - Hasselt University
Ecologist: Alan Feest - Bristol
2. Corn cultivation in US: food and agri-fuels
Economist: Steven van Passel - Hasselt University
Ecologist: Zoltan Szabo - Corvinus University
3. Life cycle assessment data
Economist:Jacob Park - consultant
Ecologist: Frederiek van Lienen - Wageningen
4. Barley production in Rajasthan, India
Economist: Dan van der Horst - Birmingham
Ecologist: Colm Bowe - Liverpool John Moores
5. Soy production in Mata Grosso, Brazil
Economist: Luke Brander
Ecologist: Zoe Davies
